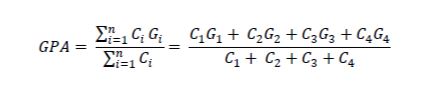The department of Civil Engineering, UIU designed a balanced and reasonably complete curriculum for the undergraduate students which will help the graduates to meet the competency level defined by international standards set by different agencies: University Grant Commission of Bangladesh, Washington Accord and ABET.
Academic Calendar
The BSc in Civil Engineering is a 4-year program. Each academic year comprises two semesters: Spring (typically January to June) and Fall (typically July to December). In every semester, the duration of the classes is fourteen (14) weeks.
Duration of semesters
Duration of the semester is generally 19 weeks, which is organized in the following way:
| Classes | 14 weeks |
| Mid Semester Examination | 2 weeks |
| Final Examination | 3 weeks |
| Total | 19 weeks |
Mid Semester Examination is held according to the academic calendar, normally after 7 weeks of class.
Types of Courses
A number of compulsory courses are identified as core courses, which form the nucleus of the bachelor degree program. Apart from the core courses, students will have to complete a number of courses, which are optional in nature. Hence students have some choices in selecting courses from a specified group or a number of courses. To understand the underpinning theory of the courses of Civil Engineering, a number of courses on mathematics, general education (social science, business, arts and humanities) and basic science have been felt mandatory to include in the curriculum. In addition, some courses related to Civil Engineering Practices (e.g., Project Planning and Management, Professional Ethics, Professional Practices and Communication) have been incorporated in the curriculum. The following Table shows the item wise distribution of the credit hours for the CE curriculum.
| Sl.No. | Group | Theory | Lab | Project | Total |
| 1 | Language | 6 | — | — | 6 |
| 2 | Mathematics | 12 | — | — | 12 |
| 3 | Basic Sciences | 6 | 3 | — | 9 |
| 4 | General Education | 11 | — | — | 11 |
| 5 | Civil Engineering Basic | 24 | 13.5 | — | 37.5 |
| 6 | Civil Engineering Core | 39 | 10.5 | — | 49.5 |
| 7 | Civil Engineering Electives | 8 | — | — | 8 |
| 8 | Civil Engineering Practices | 6 | 1.5 | — | 7.5 |
| 9 | Final Year Design Project | — | — | 6 | 6 |
| 10 | Other Engineering | 2 | 3 | — | 5 |
| Total | 114 | 31.5 | 6 | 151.5 |
Grading and Performance Evaluation
Grading System
The performance of a student in a given course is made through continuous evaluation that comprises quizzes/ in-course tests, class participation, attendance, homework/assignment, case study, mid-terms and semester final examinations. Letter grades and grade points are used to evaluate the performance of a student in a given course. The table below shows the grading policy.
| Letter Grade | Grade Point | Assessment |
| A | 4.00 | Outstanding |
| A- | 3.67 | Excellent |
| B+ | 3.33 | Very Good |
| B | 3.00 | Good |
| B- | 2.67 | Above Average |
| C+ | 2.33 | Average |
| C | 2.00 | Below Average |
| C- | 1.67 | Poor |
| D+ | 1.33 | Very poor |
| D | 1.00 | Pass |
| F | 0.00 | Fail |
Assessment Methods
For theoretical courses, assessment is generally made through continuous class assessment (i.e., class performance, assignments, and class tests), a mid-term examination and a final examination. The percentile distribution of marks for a theoretical course is as follows:
| Assessment Types | Marks |
| Class Attendance | 5% |
| Assignment | 5% |
| Class Tests | 20% |
| Mid Term | 30% |
| Final Exam | 40% |
For Lab courses assessment is generally made through continuous class assessment (e.g., class performance, report writing, viva and presentation on project), a mid-term examination and a final examination. The percentile distribution of marks for a Lab course is as follows:
| Assessment Types | Marks |
| Class Attendance | 5% |
| Class Performance/ Viva | 20% |
| Report | 25% |
| Mid Term | 20% |
| Final Exam | 30% |
Calculation of GPA/CGPA
Grade Point Average (GPA) is the weighted average grade of a semester while Cumulative Grade Point Average (CGPA) is the weighted average of the grade points obtained in all the courses completed by a student in all the semesters. For example, if a student passes/completes four courses in a semester having credits of C1, C2, C3 and C4, and his grade points in these courses are G1, G2, G3 and G4 respectively then his GPA will be calculated as follows: